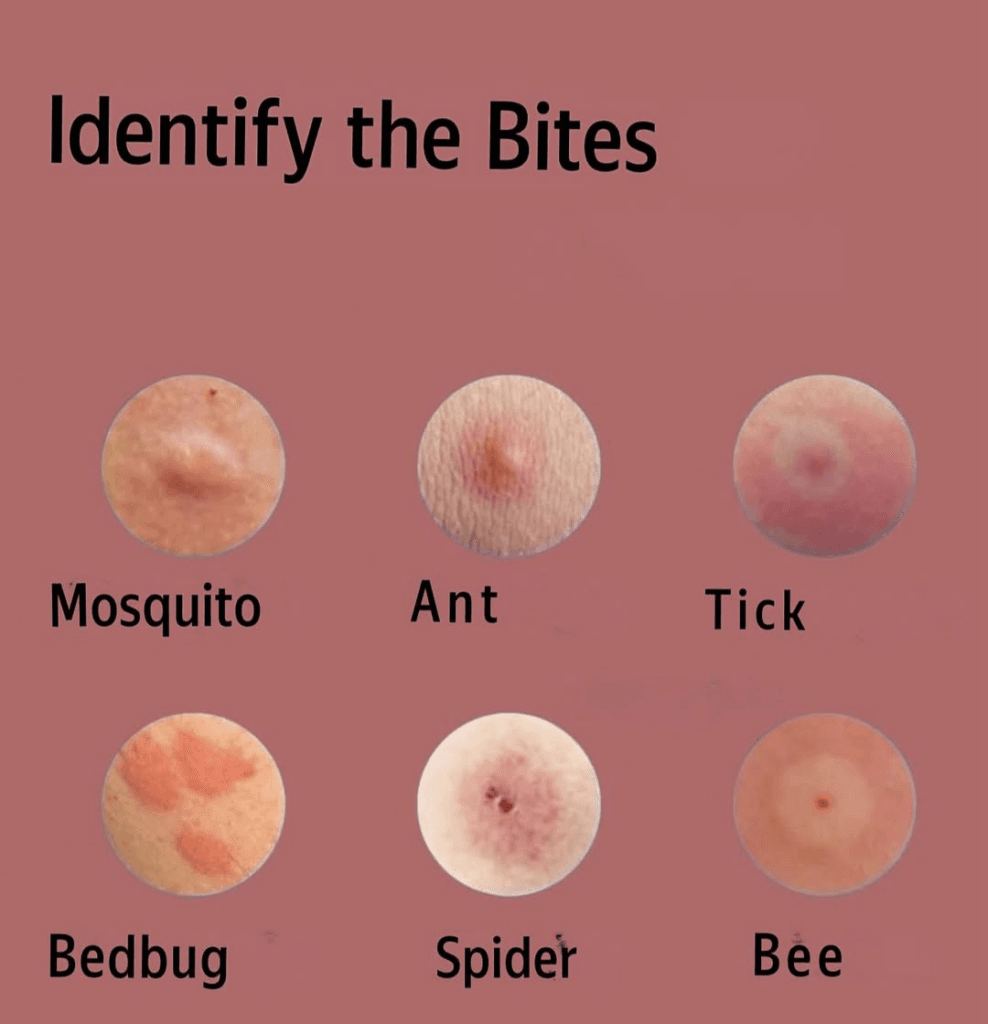
Tick Bites
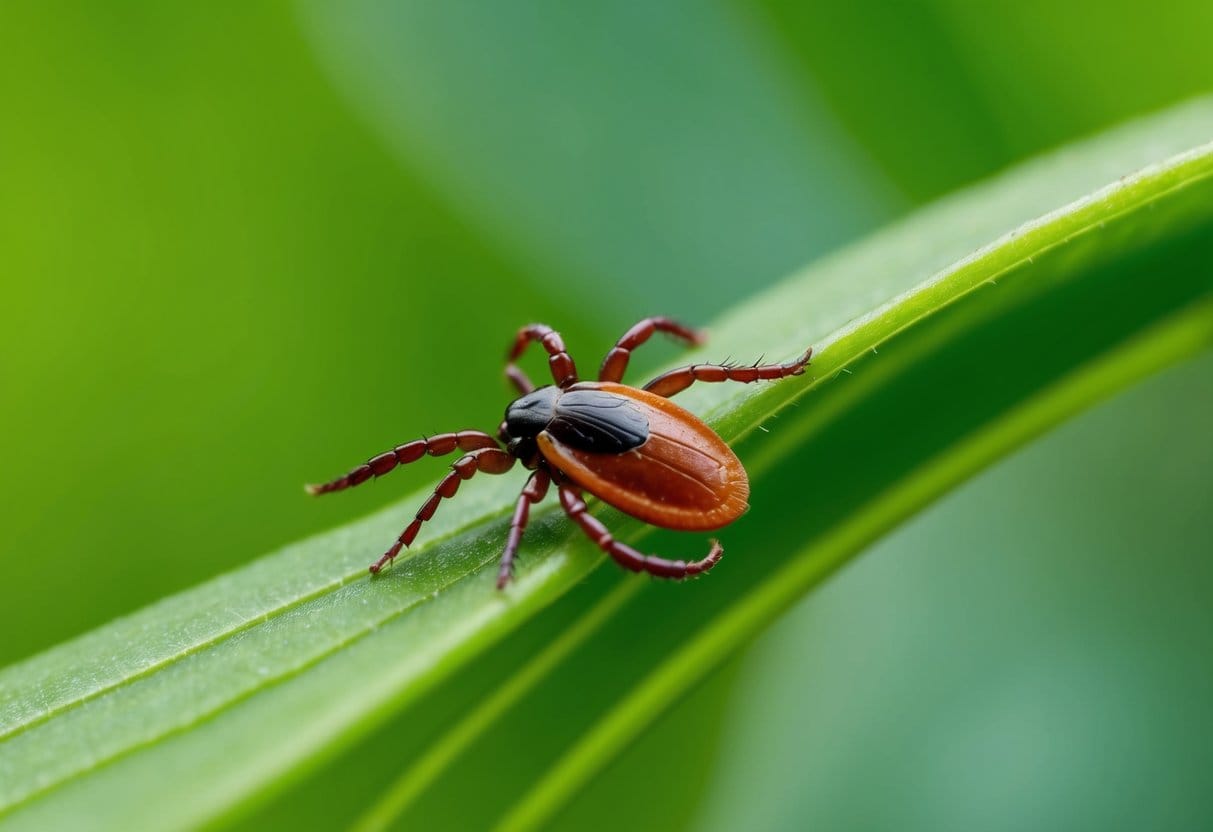

Ticks are small parasites that attach to skin and feed on blood for several days. You may feel a slight itch when bitten, but many tick bites go unnoticed. These pests often target warm body areas like:
- Hairline
- Armpits
- Behind knees
- Groin area
The best way to identify a tick bite is finding the actual tick attached to your skin. Some bites leave a small red spot about the size of a dime, but this doesn’t always happen.
While initially harmless, tick bites can lead to serious health problems. The bullseye rash is a key sign of Lyme disease, which is transmitted by certain tick species. Other concerning illnesses include:
| Disease | Common Carrier |
|---|---|
| Lyme disease | Blacklegged tick |
| Ehrlichiosis | Lone star tick |
| Anaplasmosis | Blacklegged tick |
| Tularemia | Various tick species |
Unlike most insect bites that cause immediate reactions, tick bite symptoms often develop gradually. They can appear days or even weeks after the initial bite occurred.
Spider Bites

Spider bites typically appear as two small puncture marks on the skin, often accompanied by redness and swelling. Most spiders only bite when they feel threatened or disturbed.
Common spider bite symptoms include:
- Mild pain similar to a bee sting
- Itching around the bite area
- Redness and swelling
Dangerous spider bites require immediate attention. The brown recluse spider can cause necrotic lesions where tissue dies around the bite. Black widow bites may lead to more serious symptoms:
- Muscle spasms
- Tremors
- Nausea
- Severe pain
Most spider bites heal on their own with basic care. However, if you suspect a bite from a dangerous spider like a brown recluse or black widow, seek medical attention immediately.
To identify spider bites correctly, look for the characteristic double puncture mark pattern that distinguishes them from other insect bites.
Mosquito Bites
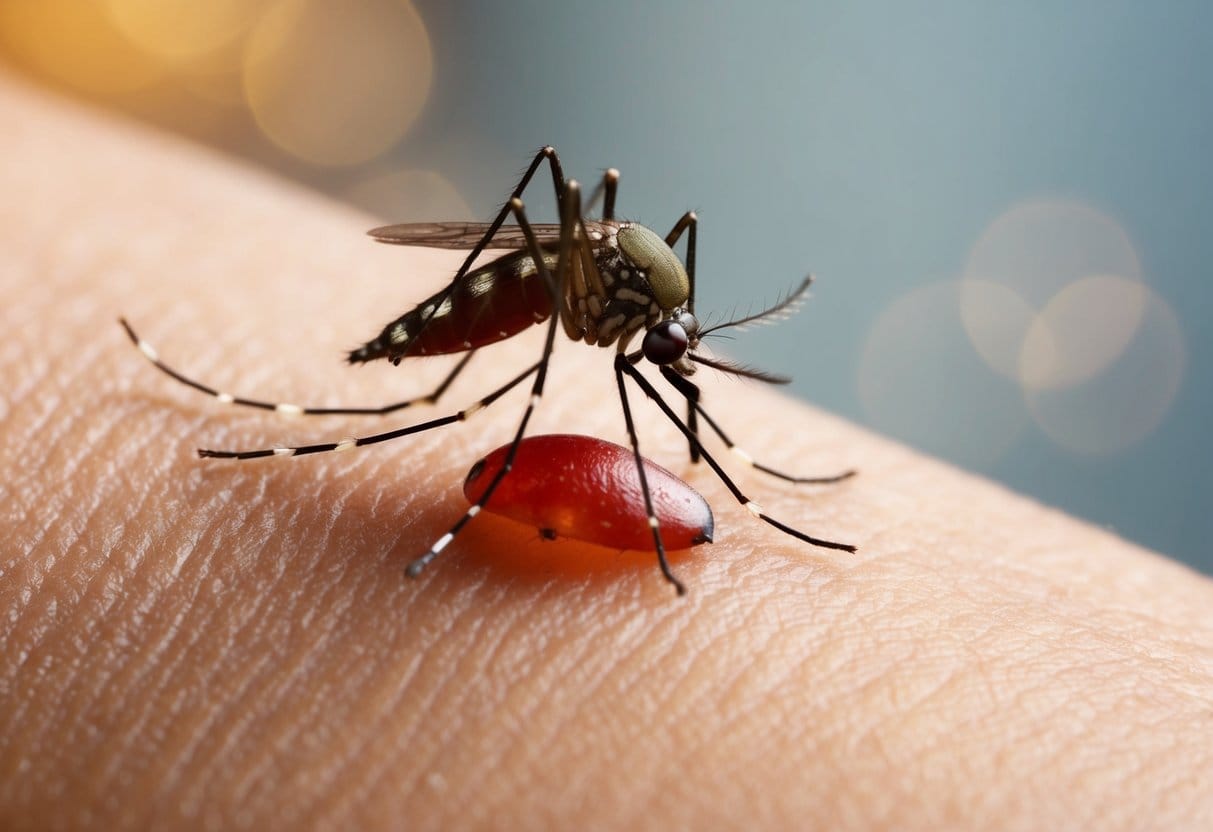
Mosquito bites typically appear as small, puffy bumps that look lighter or redder than your normal skin tone. These pesky insects often target specific areas of the body including:
- Ankles
- Hairlines
- Back of knees
- Neck
When mosquitoes bite, you won’t feel pain immediately. Later, the area becomes intensely itchy. Bites usually appear individually rather than in clusters, unless you were in a mosquito-heavy area during their most active times (dawn and dusk).
Some people experience severe reactions called “skeeter syndrome,” where bites develop into painful, swollen welts. This happens when the body has a stronger allergic response to mosquito saliva.
Health risks: Mosquitoes can transmit diseases like West Nile and Zika. Watch for any flu-like symptoms that develop after being bitten, including fever, headache, or body aches.
Bed Bug Bite Characteristics
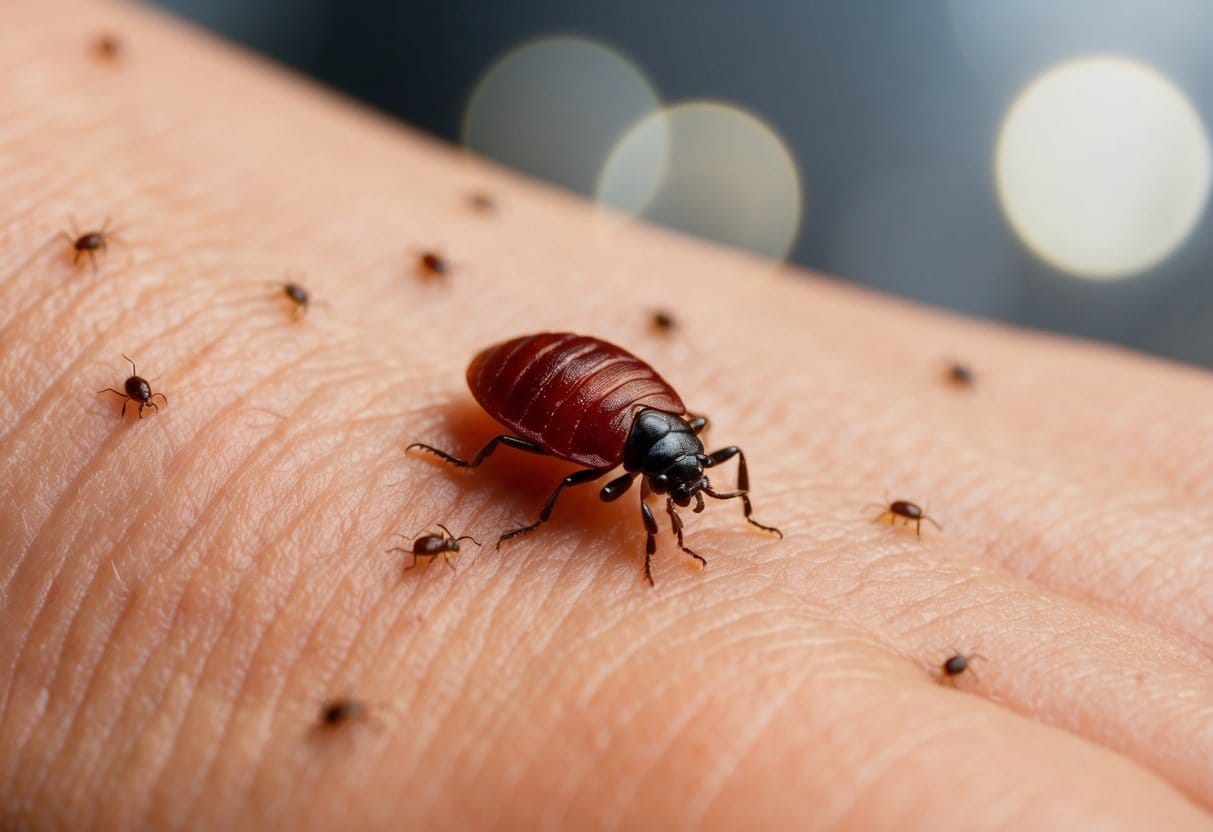

Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, raised bumps that form in distinctive linear patterns or clusters. Many people confuse these bites with mosquito bites, but the clustered arrangement—often in groups of three or more—can help identify them.
These pesky parasites tend to target exposed skin areas that make contact with bedding during sleep, including:
- Arms
- Neck
- Upper body
Bed bug bites may not hurt much when they occur, but they often become:
- Itchy
- Swollen
- Red with distinct marks at the center
Unlike other biting insects such as ticks, bed bugs don’t transmit diseases. However, they create significant discomfort and can be exceptionally difficult to eliminate. The bites themselves may appear immediately or develop several weeks after being bitten.
If you suspect bed bugs, examine your mattress carefully, focusing on corners, seams, and the headboard area where these insects and their droppings commonly hide.
Head Lice Bites
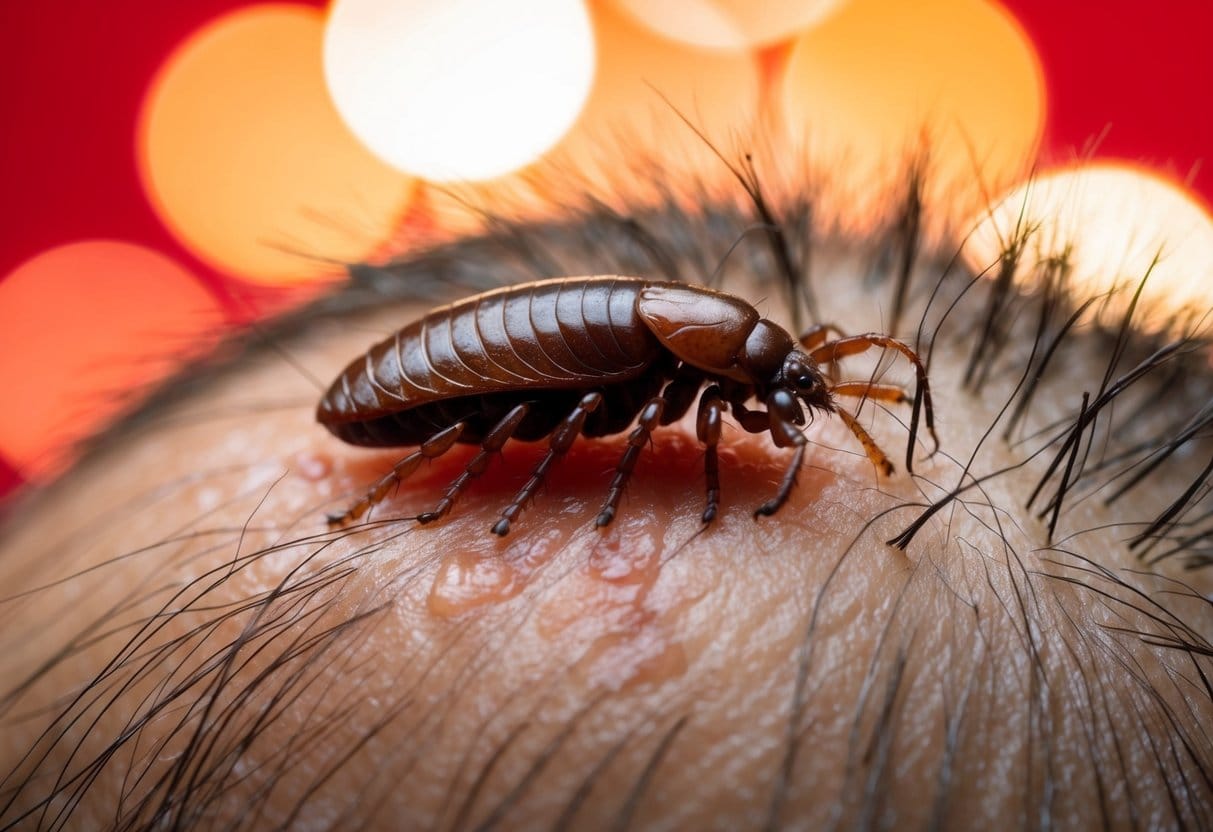

Head lice create small red spots on the scalp and nearby skin areas. These bites might be hard to spot at first, but they tend to grow larger as your body reacts to them. Many people notice the tiny eggs (nits) in hair before seeing actual bite marks.
Common symptoms include:
- Intense itching of the scalp
- Tickling sensation or feeling of movement in hair
- Sleep disturbances due to discomfort
- Open sores from scratching
The itchiness from lice bites results from their saliva during feeding. Finding clusters of itchy spots on your head is a strong indication of a lice infestation.
If you suspect head lice, it’s important to check thoroughly. The only effective solution is to eliminate the infestation completely and promptly. Delaying treatment can lead to more discomfort and potential skin infections from excessive scratching.
Flea Bites

Flea bites appear as tiny red bumps arranged in lines or clusters on the skin. These small irritations often have a distinctive reddish halo around them. Fleas typically target:
- Ankles
- Knees
- Groin area
- Armpits
- Other warm body areas
While fleas prefer animals, they can bite humans too. The bites cause intense itching that may develop into soreness or pain. Some people experience a rash around the affected skin. Be careful not to scratch these bites, as this can worsen symptoms and potentially lead to infection.
Unlike random mosquito bites, flea bites typically cluster together in specific body areas, making them easier to identify with their characteristic pattern and appearance.
Fly Bites

Fly bites often appear as raised, red bumps or welts on the skin. In some cases, these bites may bleed. Different species leave different marks, with blackfly bites typically causing more swelling than others.
Pain is the most common initial symptom of a fly bite. After the pain fades, itchiness might develop, though most bites are harmless.
Common biting flies in the United States include:
- Deer flies
- Horseflies (known for particularly painful bites)
- Stable flies
- Black flies
While rare, some fly bites can cause more serious issues. Deer flies occasionally transmit tularemia, a bacterial disease that produces painful ulcers. Black flies might cause “blackfly fever,” which resembles flu symptoms.
Most fly bites heal on their own with basic care, though severe reactions may require medical attention.
Sand Fly Bites

Sand fly bites often appear as small, red bumps or blisters that can be found alone or in clusters on the skin. These bites typically cause:
- Pain at the bite site
- Itching that develops shortly after being bitten
- Red, raised skin that may form small blisters
Sand flies are concerning in tropical, subtropical, and southern European regions where they can transmit leishmaniasis, a parasitic infection. This condition causes skin lesions and ulcers that require medical attention.
Unlike some insect bites, sand fly bites are usually quite painful when they occur, making them noticeable right away.
Chigger Bites

Chiggers are tiny red mites barely visible to the human eye, sometimes called berry bugs or harvest mites. When they bite, they create small, red marks that can appear as:
- Flat, reddish patches
- Raised, red bumps
- Occasionally blisters or pustules
These bites commonly occur in specific body areas:
- Ankles
- Wrists
- Behind the knees
- Waist
- Groin
- Lower legs
Chiggers don’t burrow under the skin or consume blood. However, their bites cause intense itching that may persist for up to two weeks. In the United States, these mites don’t transmit diseases to humans. Bites often appear in clusters, making them easier to identify compared to some other insect bites.
Ant Bites and Stings

Ant encounters can sometimes leave more than just memories. Fire ants, particularly common in southern regions, are known for their aggressive behavior and painful attacks. These tiny creatures use a two-step attack method:
- Bite – They grip your skin with their jaws
- Sting – They inject venom through their stinger
The result of these attacks often appears as a raised, pimple-like pustule on the skin, though sensitivity varies from person to person.
Fire ant stings are especially painful due to their potent venom. Since ants retain their stingers, multiple wounds often occur during a single encounter. Look for these symptoms:
| Symptom | Duration |
|---|---|
| Pain | Immediate |
| Swelling | 1-2 days |
| Inflammation | Several days to weeks |
For many people, these symptoms resolve naturally. However, the pain and inflammation may persist for days or even weeks. In some cases, medical attention becomes necessary, especially if you experience severe reactions or if the symptoms don’t improve.
Bee Stings

Bee stings appear differently depending on the person. You might see just a small light spot, or a larger red welt. Many people notice a white dot at the center where the stinger entered the skin. With honey bees specifically, the barbed stinger often remains in the skin and continues releasing venom until removed.
When stung, you’ll typically experience:
- Moderate pain
- Redness around the site
- Possible swelling
Most bee sting reactions are mild and improve within a few hours. However, serious allergic reactions can occur.
Warning signs to watch for:
- Swelling beyond the sting area
- Chest or throat tightness
- Breathing difficulties
If you notice these symptoms of anaphylaxis after being stung, call 911 immediately. This is a medical emergency requiring prompt attention.
For honey bee stings, carefully remove the stinger by scraping it away with a flat-edged object rather than using tweezers, which can squeeze more venom into the skin.
Scabies

Scabies is a skin problem caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin. These microscopic creatures can live on your skin for months if not treated. They create tunnel-like patterns as they move under your skin and lay eggs.
The main sign of scabies is an itchy, red rash that often gets worse at night. This rash may look like:
- Small pimples
- Tiny blisters
- Scaly patches
After being exposed to scabies, you might not notice any symptoms for 2-5 weeks. If you’ve had scabies before, symptoms can appear much faster—often within 1-4 days of exposure.
Warning signs:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Red rash with pimple-like bumps
- Visible burrow lines on skin
- Sores from scratching
Constant scratching can lead to open sores that may become infected. If this happens, you’ll need to see a doctor as you might need antibiotics to treat the skin infection alongside scabies treatment.
Wasp Sting Identification and Reactions

Wasp stings typically cause immediate sharp pain followed by redness and swelling at the sting site. Most people will notice a raised welt with a small white dot in the center where the stinger entered the skin. The area may feel itchy or have a burning sensation.
For most people without allergies, these symptoms fade within a few hours. However, some individuals may experience more significant reactions.
Normal Wasp Sting Symptoms:
- Immediate sharp pain
- Redness around sting site
- Localized swelling
- Itching or burning sensation
- Small white mark at puncture point
Signs of Mild Allergic Reaction:
- Extreme redness
- Increasing swelling for 2-3 days after the sting
- Nausea or vomiting
- Symptoms lasting about a week
If you experience these milder allergic symptoms, contact your doctor for advice.
Emergency Warning Signs:
- Facial, lip, or throat swelling
- Widespread hives or itching away from sting site
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Loss of consciousness
- Nausea/vomiting
- Irregular heartbeat
These severe symptoms may indicate anaphylactic shock, a life-threatening condition requiring immediate emergency medical attention. People with known wasp allergies should carry prescribed emergency medication and seek help immediately if stung.
Yellow Jacket Stings

When a yellow jacket stings, it punctures the skin and delivers venom that causes immediate pain. The affected area typically becomes red and swollen for several hours after the sting. Many people also experience:
- Itching around the sting site
- Warmth in the affected area
- General fatigue
Warning signs requiring emergency care:
| Serious Symptoms | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Difficulty breathing or swallowing | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Throat tightness | Go to emergency room |
| Hives or unusual skin reactions | Call 911 |
| Dizziness or fainting | Emergency care needed |
| Vomiting or diarrhea | Medical help required |
These severe symptoms may indicate anaphylaxis, a dangerous allergic reaction. Unlike honeybees, yellow jackets can sting multiple times because they don’t lose their stinger after an attack, making them particularly hazardous to those with allergies.
Brown Recluse Spider Bite

The brown recluse spider (also called violin spider) measures about 1-inch long and features a distinctive violin-shaped marking on its back. These spiders prefer warm, dry environments and typically hide in undisturbed places like basements, attics, and closets.
A bite from this spider often goes unnoticed at first, as it’s usually painless initially. The bite site then follows a characteristic progression:
- Skin reddens
- Area turns white
- Develops a red “bull’s-eye” appearance
- Forms blisters
- Becomes painful
Typical symptoms appear 2-8 hours after the bite:
- Moderate to severe pain
- Itching at the bite location
- Tissue damage around the bite area
Serious complications may include:
- Fever and body aches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hemolytic anemia
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Kidney failure
Though rare, these bites can be life-threatening in some cases. The venom can cause severe skin tissue destruction (skin necrosis).
If you suspect a brown recluse bite, seek immediate medical attention. If possible, capture the spider safely for identification purposes to help medical professionals confirm the type of bite and determine appropriate treatment.
Scorpion Sting

Scorpions are distinctive arachnids with eight legs, prominent pincers, and a curved tail ending in a stinger. When a scorpion stings, the affected area typically becomes red and swollen within minutes, accompanied by intense pain.
Common symptoms include:
- Severe pain at the sting site
- Tingling or numbness
- Noticeable swelling
- Redness around the area
In rare cases, more serious symptoms may develop:
- Breathing problems
- Muscle twitching
- Excessive drooling or sweating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Accelerated heart rate
- Unusual restlessness
Children and infants tend to experience more severe reactions than adults when stung by scorpions. If you or someone else develops any serious symptoms after a scorpion sting, seek medical attention immediately. The reaction to a scorpion sting can range from mild to potentially life-threatening depending on the species and the person’s sensitivity.
Kissing Bug Bites

Kissing bugs are insects found mainly in the Americas, including parts of the United States, Mexico, and Central and South America. These bugs get their name from their tendency to bite people around the face and mouth area. They typically have:
- Cone-shaped heads
- Bodies ranging from light brown to black
- Distinctive yellow, red, or tan markings
Kissing bug bites often appear in clusters concentrated in one area. Most people experience only mild reactions to these bites, including:
| Common Symptoms | Severe Reactions (Rare) |
|---|---|
| Mild itching | Intense rash |
| Redness | Difficulty breathing |
| Slight swelling | Severe allergic response |
If someone develops breathing problems or an unusual rash after a suspected kissing bug bite, they should seek immediate medical attention. These reactions may indicate a serious allergic response to proteins in the bug’s saliva. Most bites are painless but might cause swelling and itching lasting about a week.
Black Widow Spider Bite

Black widow spiders are recognizable by their shiny black bodies and distinctive red hourglass mark on their abdomen. These spiders rarely attack humans and only bite when feeling threatened or crushed.
Bite Appearance:
- Red area with white center
- May have two small puncture marks
Common Symptoms:
- Muscle pain and spasms (arms, legs, back, abdomen)
- Tremors
- Excessive sweating
- General weakness
- Chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
While their name sounds frightening, black widows typically avoid human contact. Most bites happen when people accidentally press against the spider in hidden areas like wood piles or dark corners. If you suspect a black widow spider bite, seek medical attention promptly.
Wolf Spider Bite

Wolf spiders are large, fuzzy arachnids that can reach up to 2 inches in length with gray or brown coloring. Despite their somewhat scary appearance, these creatures rarely attack humans unless they feel threatened.
If bitten, you might notice:
- Distinctive fang marks on your skin
- Slight tearing around the bite area
- Red, tender bump
- Itching sensation
Most wolf spider bites heal naturally within 7-10 days without serious complications. These spiders aren’t venomous to humans, making their bites generally harmless.
When to seek medical attention:
- If the bite area gets larger
- If you develop breathing difficulties
- If unusual redness or swelling appears
- If an ulcer forms at the bite site
Wolf spiders exist throughout many regions of the United States. Their bites typically appear as itchy, discolored spots that don’t require medical treatment in most cases.
Why Bug Bites Trigger Reactions

When insects bite or sting, they inject substances into your skin that can cause various reactions. Your body responds to these foreign substances by activating its defense system. This explains why most people experience redness and swelling at the bite site.
Common reactions include:
- Inflammation around the bite area
- Itching (mild to severe)
- Formation of welts or raised areas
- Pain or tenderness
- Warmth at the bite site
The severity of reactions to insect bites varies greatly from person to person. Some people might barely notice a bite, while others develop intense reactions. This difference depends on individual sensitivity and immune system response.
For most people, biting pests cause only minor discomfort. However, those with allergies may experience more serious symptoms. An allergic reaction can range from extensive swelling to life-threatening responses.
Managing bite reactions:
- Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling
- Use anti-itch creams to control itching
1) Take antihistamines for allergic reactions
2) Keep the area clean to prevent infection
It’s important to monitor bug bites closely. While most heal without complications, some may become infected or trigger severe allergic responses. If you notice spreading redness, increasing pain, or systemic symptoms like fever, seek medical attention promptly.
Different insects inject different substances when they bite, which explains why mosquito bites itch differently than spider bites or bee stings. Your body recognizes each of these substances as unique invaders, creating specific reactions to each type of bite.
Frequently Asked Questions

How to Recognize Different Bug Bite Types
Bug bites often have distinct features that help with identification. Mosquito bites typically appear as small, raised bumps that itch intensely. Tick bites usually have a red spot with a clear center and may include the tick still attached. Spider bites often show two puncture marks and surrounding redness.
When identifying bites, consider:
- Location on body: Some insects bite specific areas
- Pattern of bites: Single bites versus clusters or lines
- Time of year: Certain bugs are seasonal
- Recent activities: Hiking, gardening, or sleeping in different locations
Key Features of Common Insect Bites
Each type of insect leaves characteristic marks when they bite:
| Insect | Appearance | Sensation |
|---|---|---|
| Mosquito | Small, puffy, round bump | Intense itching |
| Flea | Red spot with halo | Persistent itching |
| Fire Ant | Pustule on red base | Burning pain |
| Bee/Wasp | Red swelling with central mark | Sharp pain, then throbbing |
| Chigger | Groups of small red bumps | Severe itching |
Ant bites often cause a sharp pain and develop into a pustule within 24 hours. Flea bites typically appear in groups of three or four.
Symptoms of Allergic Reactions to Bug Bites
Allergic reactions to insect bites range from mild to severe. Watch for these warning signs:
- Mild to moderate reactions:
- Extensive swelling beyond bite area
- Hives or rash spreading from bite
- Significant itching or pain
- Severe reactions (seek immediate medical help):
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Dizziness or feeling faint
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nausea or stomach cramps
People with known insect allergies should carry prescribed emergency medication at all times.
Treatment for Significantly Swollen Bug Bites
For bites with considerable swelling:
- Clean the bite area with mild soap and water
- Apply cold compresses for 10-15 minutes to reduce swelling
1) Take antihistamines to decrease itching and swelling
2) Use over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream to reduce inflammation
Medical attention should be sought if swelling continues to increase, if there’s extreme pain, or if fever develops.
Appearance Patterns of Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites have distinctive patterns that help identify them:
- Often appear in groups of three or more. This is sometimes called the “breakfast, lunch, and dinner” pattern.
- Typically form a line or zigzag pattern.
- Usually found on exposed skin during sleep. This includes the face, neck, arms, and shoulders.
- Red, itchy welts that may develop a clear center.
- Generally painless at first but become itchy within hours.
Not everyone reacts to bed bug bites, which can make identification challenging. The presence of rust-colored spots on bedding often indicates a bed bug infestation.
Mobile App Effectiveness for Bug Bite Identification
Mobile applications for bug bite identification have varying degrees of accuracy. They are most effective when combined with other identification methods.
These apps are also better at identifying common insects than rare ones. Accuracy improves with clear, well-lit photos.
Many apps provide general guidance but recommend professional confirmation. Some include tracking features to monitor symptoms over time.
While identification apps can be helpful initial tools, they should not replace medical advice for concerning bites. Their usefulness is limited by image quality and the distinctive nature of the bite itself.